Back to all members...
Sören Mindermann
PhD, started 2019

Sören is a DPhil student in CS supervised by Yarin Gal from OATML and Allan Dafoe from Oxford’s Centre for the Governance of AI. His interests in machine learning include its economic and political properties, how it scales, and safety. Before joining OATML, he worked on reward inference and machine learning for game theory with David Duvenaud and Roger Grosse at Toronto’s Vector Institute, with the Center for Human-compatible AI at UC Berkeley, and at the Future of Humanity Institute at Oxford. He has degrees in machine learning (UCL), maths (Amsterdam) and Future Planet Studies (Amsterdam). Sören is co-funded by Oxford and DeepMind.
News items mentioning Sören Mindermann • Publications while at OATML • Reproducibility and Code • Blog Posts
News items mentioning Sören Mindermann:
OATML researchers advise UK Cabinet Office
24 Sep 2021
Jan Brauner and Sören Mindermann have presented their work with Professor Yarin Gal and other collaborators on the effectiveness of mask-wearing at reducing COVID-19 transmission to the UK Cabinet Office and advised the office on mask-wearing policies.

ICML 2021
17 Jul 2021
Seven papers with OATML members accepted to ICML 2021, together with 14 workshop papers. More information in our blog post.

OATML researchers publish paper in Science
15 Dec 2020
The paper called “Inferring the effectiveness of government interventions against COVID-19” was published in Science today. The work is a collaboration with researchers from 9 universities, led by OATML graduate students Sören Mindermann and Jan Brauner, together with Mrinank Sharma from the Department of Statistics.

OATML researchers invited to speak at the German Centre for Infection Research
26 Oct 2020
OATML graduate students Sören Mindermann and Jan Brauner, together with Mrinank Sharma from the Department of Statistics, were invited to give a talk about their work with Professor Yarin Gal on ‘inferring the effects of non-pharmaceutical interventions against COVID-19’, at the German Centre for Infection Research/University of Cologne.

OATML researchers to speak at Africa CDC on COVID-19
06 Jun 2020
OATML graduate students Jan Brauner and Sören Mindermann will give an invited talk at Africa CDC, Africa’s intercontinental public health agency, on June 12. They will present their work with Professor Yarin Gal on nonpharmacetical interventions against COVID-19 to the COVID-19 modelling group.
Publications while at OATML:
Understanding the effectiveness of government interventions against the resurgence of COVID-19 in Europe
Governments are attempting to control the COVID-19 pandemic with nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs). However, the effectiveness of different NPIs at reducing transmission is poorly understood. We gathered chronological data on the implementation of NPIs for several European, and other, countries between January and the end of May 2020. We estimate the effectiveness of NPIs, ranging from limiting gathering sizes, business closures, and closure of educational institutions to stay-at-home orders. To do so, we used a Bayesian hierarchical model that links NPI implementation dates to national case and death counts and supported the results with extensive empirical validation. Closing all educational institutions, limiting gatherings to 10 people or less, and closing face-to-face businesses each reduced transmission considerably. The additional effect of stay-at-home orders was comparatively small.
Mrinank Sharma, Sören Mindermann, Charlie Rogers-Smith, Gavin Leech, Benedict Snodin, Janvi Ahuja, Jonas B. Sandbrink, Joshua Teperowsky Monrad, George Altman, Gurpreet Dhaliwal, Lukas Finnveden, Alexander John Norman, Sebastian B. Oehm, Julia Fabienne Sandkühler, Laurence Aitchison, Tomas Gavenciak, Thomas Mellan, Jan Kulveit, Leonid Chindelevitch, Seth Flaxman, Yarin Gal, Swapnil Mishra, Samir Bhatt, Jan Brauner
Nature Communications (2021) 12: 5820
[Paper]
Changing composition of SARS-CoV-2 lineages and rise of Delta variant in England
Background Since its emergence in Autumn 2020, the SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern (VOC) B.1.1.7 (WHO label Alpha) rapidly became the dominant lineage across much of Europe. Simultaneously, several other VOCs were identified globally. Unlike B.1.1.7, some of these VOCs possess mutations thought to confer partial immune escape. Understanding when and how these additional VOCs pose a threat in settings where B.1.1.7 is currently dominant is vital. Methods We examine trends in the prevalence of non-B.1.1.7 lineages in London and other English regions using passive-case detection PCR data, cross-sectional community infection surveys, genomic surveillance, and wastewater monitoring. The study period spans from 31st January 2021 to 15th May 2021. Findings Across data sources, the percentage of non-B.1.1.7 variants has been increasing since late March 2021. This increase was initially driven by a variety of lineages with immune escape. From mid-April, B.1.617.2 (WHO label Delta) spread ra... [full abstract]
Swapnil Mishra, Sören Mindermann, Mrinank Sharma, Charles Whittaker, Thomas A. Mellan, Thomas Wilton, Dimitra Klapsa, Ryan Mate, Martin Fritzsche, Maria Zambon, Janvi Ahuja, Adam Howes, Xenia Miscouridou, Guy P. Nason, Oliver Ratmann, Elizaveta Semenova, Gavin Leech, Julia Fabienne Sandkühler, Charlie Rogers-Smith, Michaela Vollmer, H. Juliette T. Unwin, Yarin Gal, Meera Chand, Axel Gandy, Javier Martin, Erik Volz, Neil M. Ferguson, Samir Bhatt, Jan Brauner, Seth Flaxman
EClinicalMedicine (2021), 39:101064
[Paper]
Is the cure really worse than the disease? The health impacts of lockdowns during COVID-19
During the pandemic, there has been ongoing and contentious debate around the impact of restrictive government measures to contain SARS-CoV-2 outbreaks, often termed ‘lockdowns’. We define a ‘lockdown’ as a highly restrictive set of non-pharmaceutical interventions against COVID-19, including either stay-at-home orders or interventions with an equivalent effect on movement in the population through restriction of movement. While necessarily broad, this definition encompasses the strict interventions embraced by many nations during the pandemic, particularly those that have prevented individuals from venturing outside of their homes for most reasons. The claims often include the idea that the benefits of lockdowns on infection control may be outweighed by the negative impacts on the economy, social structure, education and mental health. A much stronger claim that has still persistently appeared in the media as well as peer-reviewed research concerns only health effects: that there... [full abstract]
Gideon Mayerowitz-Katz, Samir Bhatt, Oliver Ratmann, Jan Brauner, Seth Flaxman, Swapnil Mishra, Mrinank Sharma, Sören Mindermann, Valerie Bradley, Michaela Vollmer, Lea Merone, Gavin Yamey
BMJ Global Health, 2021, 6:e006653
[Paper]
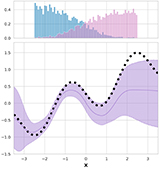
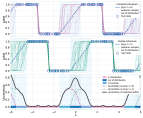
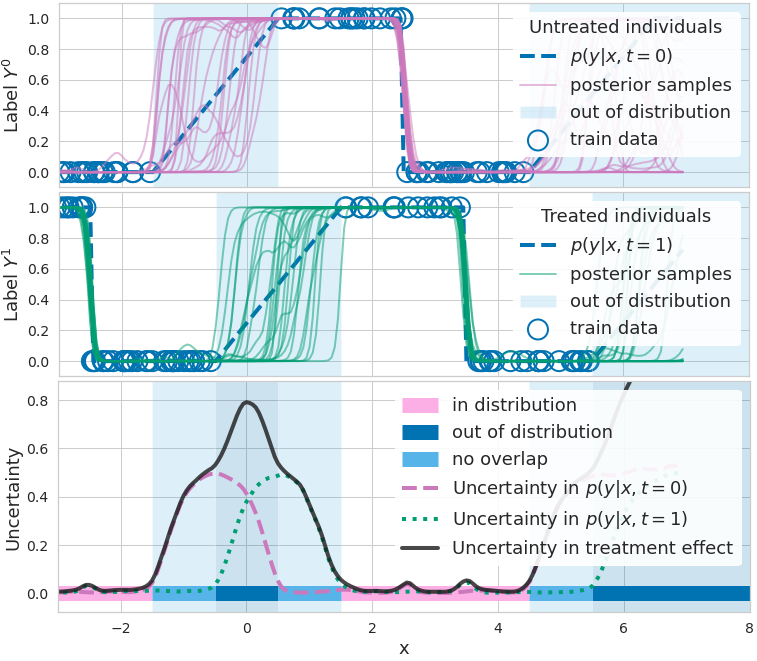
Quantifying Ignorance in Individual-Level Causal-Effect Estimates under Hidden Confounding
We study the problem of learning conditional average treatment effects (CATE) from high-dimensional, observational data with unobserved confounders. Unobserved confounders introduce ignorance -- a level of unidentifiability -- about an individual's response to treatment by inducing bias in CATE estimates. We present a new parametric interval estimator suited for high-dimensional data, that estimates a range of possible CATE values when given a predefined bound on the level of hidden confounding. Further, previous interval estimators do not account for ignorance about the CATE stemming from samples that may be underrepresented in the original study, or samples that violate the overlap assumption. Our novel interval estimator also incorporates model uncertainty so that practitioners can be made aware of out-of-distribution data. We prove that our estimator converges to tight bounds on CATE when there may be unobserved confounding, and assess it using semi-synthetic, high-dimensional ... [full abstract]
Andrew Jesson, Sören Mindermann, Yarin Gal, Uri Shalit
ICML, 2021
[arXiv]
Understanding the effectiveness of government interventions in Europe's second wave of COVID-19
As European governments face resurging waves of COVID-19, non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) continue to be the primary tool for infection control. However, updated estimates of their relative effectiveness have been absent for Europe's second wave, largely due to a lack of collated data that considers the increased subnational variation and diversity of NPIs. We collect the largest dataset of NPI implementation dates in Europe, spanning 114 subnational areas in 7 countries, with a systematic categorisation of interventions tailored to the second wave. Using a hierarchical Bayesian transmission model, we estimate the effectiveness of 17 NPIs from local case and death data. We manually validate the data, address limitations in modelling from previous studies, and extensively test the robustness of our estimates. The combined effect of all NPIs was smaller relative to estimates from the first half of 2020, indicating the strong influence of safety measures and individual protect... [full abstract]
Mrinank Sharma, Sören Mindermann, Charlie Rogers-Smith, Gavin Leech, Benedict Snodin, Janvi Ahuja, Jonas B. Sandbrink, Joshua Teperowski Monrad, George Altman, Gurpreet Dhaliwal, Lukas Finnveden, Alexander John Norman, Sebastian B. Oehm, Julia Fabienne Sandkühler, Thomas Mellan, Jan Kulveit, Leonid Chindelevitch, Seth Flaxman, Yarin Gal, Swapnil Mishra, Jan Brauner, Samir Bhatt
MedRxiv
[Paper]
Inferring the effectiveness of government interventions against COVID-19
Governments are attempting to control the COVID-19 pandemic with nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs). However, the effectiveness of different NPIs at reducing transmission is poorly understood. We gathered chronological data on the implementation of NPIs for several European, and other, countries between January and the end of May 2020. We estimate the effectiveness of NPIs, ranging from limiting gathering sizes, business closures, and closure of educational institutions to stay-at-home orders. To do so, we used a Bayesian hierarchical model that links NPI implementation dates to national case and death counts and supported the results with extensive empirical validation. Closing all educational institutions, limiting gatherings to 10 people or less, and closing face-to-face businesses each reduced transmission considerably. The additional effect of stay-at-home orders was comparatively small.
Jan Brauner, Sören Mindermann, Mrinank Sharma, David Johnston, John Salvatier, Tomáš Gavenčiak, Anna B Stephenson, Gavin Leech, George Altman, Vladimir Mikulik, Alexander John Norman, Joshua Teperowski Monrad, Tamay Besiroglu, Hong Ge, Meghan A Hartwick, Yee Whye Teh, Leonid Chindelevitch, Yarin Gal, Jan Kulveit
Science (2020): eabd9338
[Paper]
On the robustness of effectiveness estimation of nonpharmaceutical interventions against COVID-19 transmission
There remains much uncertainty about the relative effectiveness of different nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) against COVID-19 transmission. Several studies attempt to infer NPI effectiveness with cross-country, data-driven modelling, by linking from NPI implementation dates to the observed timeline of cases and deaths in a country. These models make many assumptions. Previous work sometimes tests the sensitivity to variations in explicit epidemiological model parameters, but rarely analyses the sensitivity to the assumptions that are made by the choice the of model structure (structural sensitivity analysis). Such analysis would ensure that the inferences made are consistent under plausible alternative assumptions. Without it, NPI effectiveness estimates cannot be used to guide policy. We investigate four model structures similar to a recent state-of-the-art Bayesian hierarchical model. We find that the models differ considerably in the robustness of their NPI effectiveness ... [full abstract]
Mrinank Sharma, Sören Mindermann, Jan Brauner, Gavin Leech, Anna B. Stephenson, Tomáš Gavenčiak, Jan Kulveit, Yee Whye Teh, Leonid Chindelevitch, Yarin Gal
NeurIPS, 2020
[Paper]
Identifying Causal Effect Inference Failure with Uncertainty-Aware Models
Recommending the best course of action for an individual is a major application of individual-level causal effect estimation. This application is often needed in safety-critical domains such as healthcare, where estimating and communicating uncertainty to decision-makers is crucial. We introduce a practical approach for integrating uncertainty estimation into a class of state-of-the-art neural network methods used for individual-level causal estimates. We show that our methods enable us to deal gracefully with situations of "no-overlap", common in high-dimensional data, where standard applications of causal effect approaches fail. Further, our methods allow us to handle covariate shift, where test distribution differs to train distribution, common when systems are deployed in practice. We show that when such a covariate shift occurs, correctly modeling uncertainty can keep us from giving overconfident and potentially harmful recommendations. We demonstrate our methodology with a ra... [full abstract]
Andrew Jesson, Sören Mindermann, Uri Shalit, Yarin Gal
NeurIPS, 2020
[arXiv] [BibTex]
Blog Posts
21 OATML Conference and Workshop papers at ICML 2021
OATML group members and collaborators are proud to present 21 papers at ICML 2021, including 7 papers at the main conference and 14 papers at various workshops. Group members will also be giving invited talks and participate in panel discussions at the workshops. …
Full post...Angelos Filos, Clare Lyle, Jannik Kossen, Sebastian Farquhar, Tom Rainforth, Andrew Jesson, Sören Mindermann, Tim G. J. Rudner, Oscar Key, Binxin (Robin) Ru, Pascal Notin, Panagiotis Tigas, Andreas Kirsch, Jishnu Mukhoti, Joost van Amersfoort, Lisa Schut, Muhammed Razzak, Aidan Gomez, Jan Brauner, Yarin Gal, 17 Jul 2021
When causal inference fails - detecting violated assumptions with uncertainty-aware models
NeurIPS 2020. Tl;dr: Uncertainty-aware deep models can identify when some causal-effect inference assumptions are violated. …
Full post...Andrew Jesson, Sören Mindermann, Uri Shalit, Yarin Gal, 08 Dec 2020
22 OATML Conference and Workshop papers at NeurIPS 2020
OATML group members and collaborators are proud to be presenting 22 papers at NeurIPS 2020. Group members are also co-organising various events around NeurIPS, including workshops, the NeurIPS Meet-Up on Bayesian Deep Learning and socials. …
Full post...Muhammed Razzak, Panagiotis Tigas, Angelos Filos, Atılım Güneş Baydin, Andrew Jesson, Andreas Kirsch, Clare Lyle, Freddie Kalaitzis, Jan Brauner, Jishnu Mukhoti, Lewis Smith, Lisa Schut, Mizu Nishikawa-Toomey, Oscar Key, Binxin (Robin) Ru, Sebastian Farquhar, Sören Mindermann, Tim G. J. Rudner, Yarin Gal, 04 Dec 2020