Virtual Assay is a powerful tool that allows the user to simulate "in silico" drug assays with a friendly and easy to use interface. This software is currently being used in many evaluation studies in collaboration with pharma companies.
In our recent paper in Frontiers in Physiology we used Virtual Assay to run human in silico drug trials for more than 60 compounds, and we demonstrated that we can predict clinical risk of arrhythmias with higher accuracy than animal experiments. Check our results here:
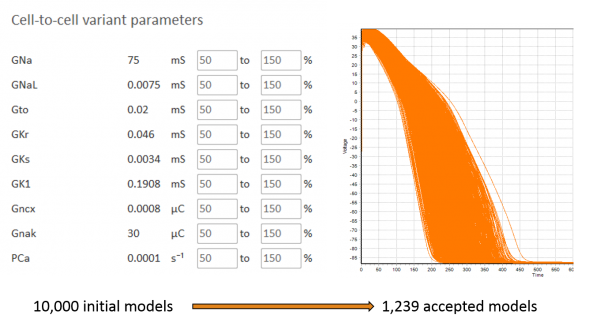
In this case study we simulated the effects of Dofetilide on the human ventricular action potential at a population level of single cardiac cells.
We simulated 4 different drug concentrations (0.1 to 100 nM) based on the experimentaly measured ways of action of Dofetilide on human ion channels (potent inhibitor of the rapid delayed rectifier potassium current). To simulate a specific drug, Virtual Assay allows for an easy introduction of parameters related to drug action on each ionic current (IC50 and Hill coefficient).

In this case study we simulated the effects of Flecainide on the human ventricular action potential at a population level of single cardiac cells.
We simulated 3 different drug concentrations (0.1 to 10 uM) based on the measured ways of action of Flecainide on human ion channels (mainly an inhibitor of the rapid delayed rectifier potassium current, but also a milder inhibitor of the fast sodium and L-type calcium currents).
The following figure shows action potential prolongation at 90% of repolarization (APD90) from control to the highest Flecainide dose. Other important drug markers can also be quantified by Virtual Assay. The following figure illustrates the case of maximum upstroke velocity, related to drug action during depolarisation (fast sodium current block).
Finally, Flecainide effects on an action potential human model are illustrated in the figure below for different drug concentrations.